First scan after a positive pregnancy test
In the first trimester of pregnancy, an early ultrasound can be performed at 6 to 9 weeks. This scan allows you and your partner to have the first glimpse of your growing baby and it can be used to:
- Estimate the due date
- Confirm the baby’s heartbeat
- Check the pregnancy’s location to ensure it is in the right location – inside the uterus (if it is not in the right position, it is called a tubal or ectopic pregnancy)
Screening for Down Syndrome
- A NT Scan
- The NT scan is a safe, non-invasive test that screens your baby for chromosome conditions. This scan measures the amount of fluid, called the nuchal translucency, at the back of a baby's neck.
- Excessive fluid may suggest a potential risk of Down syndrome or other chromosome conditions like Patau syndrome or Edwards syndrome.
- The NT scan cannot provide a definite diagnosis for these conditions or other chromosome variations. It can only estimate the risk involved.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Test (NIPT)
- NIPT is a test that analyses small pieces of DNA in your blood to assess the risk of genetic conditions.
- The NIPT is used to screen for chromosomal conditions, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), and variations in the sex chromosomes (extra or missing copies of the X and Y chromosomes).
- The NIPT is a highly accurate screening test, but it cannot provide a definitive diagnosis. It can only predict whether the risk of a genetic condition is high or low.
A Structural Ultrasound Scan
A detailed abdominal ultrasound is usually performed around 20 weeks of pregnancy to check the baby’s growth and structural development.
The scan includes a detailed examination of various structures including the skull, orbits (eye sockets), lips, spine, heart, lung, diaphragm, stomach, kidneys, bladder, abdomen, umbilical cord, limbs, and foetal genital organs.
This can detect major structural conditions in the baby. However, not all conditions can be detected, so a normal structural ultrasound report doesn't guarantee the absence of conditions at or after birth.
Urine tests
A urine sample is collected and tested with a strip for the presence of sugar or protein at every antenatal checkup.
If detected, your doctor will arrange further tests to evaluate potential conditions such as gestational diabetes, urinary tract infections, renal disease, or pre-eclampsia.
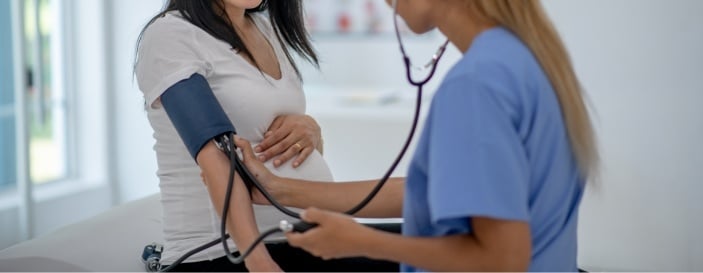
Blood pressure
Blood pressure measurement is an important part of the assessment and management of hypertensive (high blood pressure) disorders during pregnancy.
An abnormal blood pressure reading is a concern, as you and the baby may be at a higher risk of health conditions. Blood pressure is measured at each antenatal appointment to monitor and provide appropriate management if needed.
Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
GBS are bacteria that occur naturally in the intestine, urinary tract, and reproductive tract in about 15-25% of women. They are normal and rarely harmful. However, in a small number of cases (1%), the mother can pass it to the baby at birth and cause an infection that makes the baby sick.
If you test positive for GBS, you may be given antibiotics during labour to protect your baby.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
Screening test for diabetes in pregnancy (gestational diabetes) involves consuming a sugary drink and collecting 2 or 3 blood samples to assess how your body processes and stores sugar. The test is typically done after an overnight fast of 8 to 10 hours. Resting during the test is advised, as exertion can impact the results. Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting after the drink. Normal eating and drinking can be resumed after the test.
If your blood sugar levels are abnormal, you will receive guidance on managing it through self-monitoring, diet, exercise, and medications as required.
This concludes our three-part series on antenatal screening. For a comprehensive pregnancy journey, revisit our earlier articles on prenatal care and antenatal blood tests.

Preparing for parenthood
Health education is an integral part in helping prepare for the delivery of a new family member so do make sure to enrol in classes for parents such as an antenatal course , paediatric first aid course and to enroll key carers on courses such as childcare and first aid for domestic helpers. Please visit our website for details.
Delivering at Matilda
Matilda International Hospital provides a seamless, single point of care throughout your pregnancy and delivery as well as providing postnatal care at home. Learn more about our Postnatal Care services.
Our Patient Service Team will guide you through the process and help you make an informed decision on your pregnancy journey. We can arrange a private maternity tour and help with the pre-authorization with insurance companies. Please contact the Patient Service Centre at 2849 0111 if you wish to arrange a maternity tour.
Information regarding the cost of antenatal care is available here, and details about delivery with a designated obstetrician can be found here.